What is Low Code No Code application development?
For many years, businesses have had only two options when it came to application development: either they could buy pre-made apps from an outside vendor or they could build their own apps from scratch and then customize them using skilled developers and coders. Neither option was particularly appealing to businesses. But now, we are witnessing the rise of low-code no-code (LCNC) development alternatives that bring the power of application development to users across the enterprise. These alternatives are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
Users are given the ability and freedom to swiftly design applications and automate business processes by using these alternative techniques of app creation, which employ an easy and graphical interface. This eliminates the need for users to type code line by line. When LCNC tools are utilized, there is the potential for increased user accessibility, which in turn encourages more creativity and relieves stress on IT departments. The introduction of LCNC platforms is the next step toward the goal of simplifying application development so that it may be performed by anyone.
What is low code?
The term low code refers to an approach to the design and development of software programs that makes use of user-friendly graphical tools and pre-built features to reduce the amount of traditional pro-code that must be written. Although writing pro-code is still a component of the development process, low-code development provides users with an enhanced and streamlined experience that enables them to begin developing content more rapidly.
What is no code?
No-code is a strategy that provides non-technical business people with the ability to construct applications without having to write even a single line of code. This is an improvement above low-code, which only provides a similar user experience, but no-code goes one step beyond.
Low-code vs. no-code
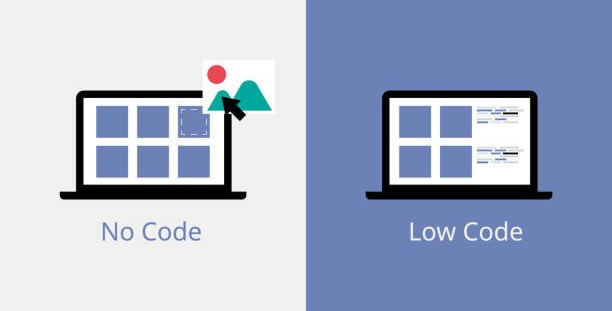
The level of coding expertise required of the user is the primary determining factor in determining whether a development platform is considered low-code or no-code. Low-code development platforms, also known as LCDPs, require users to have some knowledge of coding in order for them to be able to design and integrate complicated programs. On the other hand, no-code development platforms, also known as NCDPs, do not require any knowledge of programming at all. As a result of the fact that most companies have employees with a diverse collection of technical skill sets, several platforms have developed tools that need little to no coding at all.
The proliferation of amateur software programmers
The distinctive information and perspectives that subject-area professionals possess might be challenging to communicate properly to IT teams in many cases. Businesses can ensure that the members of their team who are the most knowledgeable can participate in the process of developing mobile applications by giving citizen developers more responsibility. And because LCNC platforms are on their side, department heads and IT experts are able to better interact with one another and make certain that the appropriate technologies, procedures, and processes are in place. The increase in the number of citizen developers helps meet the need for new applications, addresses the shortage of skilled developers, reduces the workloads of IT teams, and enables businesses to adapt more quickly to the expectations of customers and the market.
How do low code or no code tools work?
Conventional application development calls for the employment of practitioners with a high level of expertise in code-writing, and it frequently necessitates waiting in a lengthy line in the IT department in order to have new applications produced or updated.
The concepts of model-driven design, automatic code generation, and visual programming form the foundation of low-code development platforms (LCDPs) and no-code development platforms (NCDPs), respectively. Despite the fact that the users of these platforms may or may not have coding knowledge, the platforms have been purposefully built to target users who are familiar with the processes and workflows inside their business area. Again, this not only gives non-technical people more power, but it also connects them with seasoned programmers who can help them.
The following is a list of some of the most important stages in the process of developing LCNC:
Define your requirements and the outcome that you want:
It is crucial to establish the business needs and the expected outcomes of your project at the very beginning, regardless of whether you are working on an application that interacts directly with customers or an internal business procedure. What exactly is the issue that has to be fixed by this app? Who exactly is going to be using it? Which kinds of information and facts are required for its operation?
Create a diagram of the company's workflow or process: Users are able to specify and document the workflows and processes that they desire by utilizing the business process management (BPM) and development tools provided by LCNC. This is typically accomplished by determining, inside the program, which modules serve which purposes and then creating those modules as if they were separate entities. Some modules, for instance, may be responsible for data collection, while others may be responsible for initiating an action or event. At this point, the citizen developer can begin by building the system and then proceed to integrate the various components to obtain the desired result.
Put your project through its paces as an LCNC application test and deployment: Users are able to have all of the complicated back-end aspects of the process resolved with just a few clicks using the LCNC platform. When it is finished, IT specialists and/or beta testers will be able to evaluate the program, and once their suggestions have been accepted, the app will be ready to be made available to the general public.
What are some examples of how low-code and no-code app development can be used?

Recent research conducted by Gartner indicates that by the year 2024, more than sixty-five percent of all application development taking place worldwide will make use of Low Code No Code platforms. This comes with a strong growth rate projection of 165% each year for the next two years. When companies start using Low Code No Code tools, the number of citizen users quickly grows, as does their level of expertise. This is because individuals start to realize the benefits of quick and precise app creation across practically any department of any business when companies start using the tools.
Here are several examples:
Applications that can help supply chains overcome many difficulties, such as delays caused by pandemics, trade restrictions, and climate change, all of which have the potential to disrupt supply chains, can be developed. Tools available through LCNC have the potential to assist in overcoming these problems in three important ways:
Developing apps that are responsive and progressive for collaboration and end-to-end visibility, giving increased trackability, and enabling traceability back to the supply chain
Modeling, monitoring, and improving supply chain operations from the sourcing of raw materials to delivery at the customer's front door requires the creation of automated workflows and business processes.
The digitization of legacy data and records and their integration with both existing data and new data that is being received makes it possible to conduct more accurate analytics and robust data drove.
The manufacturing industry can model its processes with the help of LCNC, which can then drive the development of smart factories and digital manufacturing environments.
Robotic process automation (RPA) and Internet of Things (IoT) networks both have untapped potential that can be unlocked with the help of Low Code No Code. LCNC solutions help manufacturing processes function more smoothly and effectively in every step of the process, from the processing of raw materials to the packing and shipment of finished goods.
Teams specializing in accounting and finance are able to design bespoke business applications that are capable of supporting a diverse selection of workflows and information management procedures. For instance, an accounting firm could design a portal for tax filing by defining workflows for the process. This would allow the firm to guide clients through the process of reporting expenses and income, presenting bank statements and other financial disclosures, and getting rid of the glut of emails and printed documents.
Similarly, a financial institution may map workflows by automating loan approvals, risk assessments, decision flows, and information management. This would result in time savings for both the customers and the financial advisors.
The LCNC platform allows for the personalization of job postings, the automation of hiring procedures, the screening of candidates, and the creation of comprehensive training programs. And all of these operations may now be completed without taxing the resources of the IT teams that are responsible for them.
IT departments frequently discover that LCNC platforms may assist them in streamlining complicated procedures, thereby increasing both their efficiency and their agility. In addition, organizations will be able to lessen the amount of work they have to do if there are more citizen developers. IT departments can still keep the authority to manage and implement Low Code No Code programs, but they no longer have to deal with the tedious and time-consuming code-writing activities that are typically connected with that process. This gives IT departments a tremendous amount of newfound freedom. IT workers are being urged to view the LCNC not so much as a danger but rather as an agile work environment that provides them with the space they require to build and develop to their full potential. In point of fact, the most solid software solutions support pro-code/low-code hybrids, which is a procedure that falls somewhere in the middle and involves both IT programming expertise and the effort of citizen developers. Recent estimates suggest that collaboration between IT specialists and business users is present in more than sixty percent of all LCNC development initiatives. According to another study that was published in the Harvard Business Review, a single IT developer can provide assistance for as many as ten or more citizen developers, hence enhancing overall agility and productivity.
Initiatives to automate processes are becoming increasingly common as businesses look for ever-more-effective ways to improve their business process automation (BPA). The term "robotic process automation" (RPA) refers to self-learning software and bots that are specially intended to replicate human behaviors in the performance of ordinary and repetitive business operations. RPA is an essential component of business process automation (BPA). Reading and entering data, extracting information from documents, and doing a wide variety of other rule-based tasks are examples of what this can entail.
RPA is a useful and powerful tool; nevertheless, it is absolutely dependent on having the appropriate parameters put up in the first place in order for it to work well. While it is true that RPA bots can learn as they go, they are unable to rewrite fundamental inefficiencies in the "rules" that govern corporate processes. Here is where applications that require little to no coding come into play as a catalyst for greater process automation results. Who better than the subject-area specialists themselves to comprehend and comprehend defects and inefficiencies in their processes? These professionals have the capacity to go in with pinpoint accuracy to break down process bottlenecks and weak points thanks to the potential of LCNC to provide citizens the ability to design software. This new interpretation of the rules is subsequently communicated to the RPA bots, whose tasks have suddenly become significantly more fruitful as a result.
The primary advantages of using low-code or no-code platforms
The widespread benefits that these technologies bring to an organization are reflected in the increasing popularity of LCNC platforms. The utilization of LCNC platforms entails the following:
Because the apps are not created from start, the development process is streamlined, which makes it possible to focus more on satisfying the wants and expectations of users. This results in easier use. "Imagine a world where you do not have to write code, just say things, and the computer does it for you," Koushik Sen, a prominent computer science lecturer at the University of California, Berkeley, said in a recent interview.
Increased rate of development As a result of the ease with which users can modify and customize the primary components and fundamental code of their apps, the real rate of development is significantly increased. In addition, users are able to link and integrate apps, processes, and workflows from pre-existing applications onto the platform. Forrester found that using low-code development platforms brought about a 20-fold increase in the speed at which development projects could be completed compared to when traditional coding was used.
Increased automation: Users are able to automate the design of workflows by setting basic rules for decision-making, which can then be implemented in numerous information systems. This allows for increased efficiency. Many of the LCNC technologies make use of robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning in order to provide suggestions for automation based on previously collected data sets.
Lessening the amount of time something takes can help save money and other critical resources. The complexity of maintenance procedures is simplified thanks to LCNC, which in turn lowers costs and eases the strain on IT. In addition, you won't have to spend a lot of money to test out new concepts that come from nearly any department. These concepts have the potential to completely transform existing procedures, thereby boosting both productivity and efficiency.
Simpler data integration: The process of data integration is made easier and more flexible by the creation of workflows in which information is collected, shared, processed, and stored. Users of LCNC tools are given the ability to locate, comprehend, and make use of data within a process. You will be able to identify the source, ownership, validity, and quality of data across all processes, which will enable you to make decisions that are both more informed and more confident.
Greater dexterity: You are able to quickly respond to new opportunities and regulatory or compliance challenges when you have development that is both quick and straightforward, and this often happens in real-time. In addition, the ease of use of LCNC platforms makes it possible for developers to try out new concepts and concepts without having to make significant expenditures in information technology or other external resources. In addition, since Low Code No Code makes development simpler, this expands the pool of developers and enables more users to contribute to the production of applications through the use of technology.
A more positive experience for the customer: Both the customer experience and the customer's loyalty will improve if the company is able to keep its applications and workflows up-to-date and responsive to feedback from its customers. CX specialists can also leverage LCNC platforms to design bespoke consumer surveys, e-commerce platforms, customer service applications, and loyalty programs.
Greater privacy and security: LCNC enables firms to undertake development tasks that are either too sensitive to be outsourced to third parties or cannot be performed by unaffiliated third parties. This helps to reduce the likelihood of data breaches or other forms of cybercrime.
The most important advantages of using low-code or no-code platforms
These technologies are, without a shadow of a doubt, transforming businesses and providing them with the competitive edge they want in order to satisfy the demands of the modern market. Incorporating solutions for citizen users does, however, require a significant commitment to change management, communication, and breaking down silos. This is the case with every corporate transformation.
Concerns have been expressed in response to these recent shifts in the status quo. For instance, the widespread adoption of Low Code No Code platforms may increase the number of shadow IT projects. These are endeavors that are carried out without the knowledge or approval of the IT department. In addition, it is possible that apps developed by citizen developers were not designed with scalability in mind. Furthermore, these applications may be susceptible to obsolescence if the developer who developed them did so in a silo and later left the organization.
To start preventing problems like this from occurring, do the following:
- putting in place compliance and governance standards that support the finest IT practices and promote strong and workable collaboration models between IT, citizen developers, and their teams.
- Making certain that the efforts being put into training are both comprehensive and easily accessible. When it comes to LCNC training, the age-old proverb that begins "teach a man to fish" is a pretty relevant way to think about it. Setting up a few webinars and hoping for the best is a certain way to ensure that there will be a low uptake of the product and poor execution of the projects.
- Making contact with your software vendor, who will be able to guide you through the process of identifying the enterprise development tools that are most appropriate for your specific requirements, is a good first step.
Leave a Reply
Contact PNATC
Contact - Website lead
Recent Posts

Share Post
Contact PNATC
Get all your questions answered and problems solved with our QuickBooks experts today!