Business Process Automation
What Is Business Process Automation?
The use of the latest technologies to complete business procedures with the least amount of human participation is known as business process automation, or BPA. A business process is an action or series of actions used to fulfill a particular organizational objective, including creating a product, onboarding new staff members, or attracting clients.
A business process usually starts with an action and involves several company departments. When an employee is onboarded, for instance, the HR system might initiate a series of pre-established process steps to set up financial information in the pay system, send out a welcome email, and arrange security credentials. The productivity and accuracy of each workflow phase in the business process are usually increased by automating them.
BPA leverages a range of cutting-edge technologies, such as cloud platforms, process intelligence capabilities, and automation tools. Furthermore, BPA features are frequently added to well-known enterprise applications like human capital management systems, enterprise resource planning software, and other instruments that uphold industry best practices.
Business Process Automation Applications
Management, operations, supply chains, human resource procedures, and marketing are just some of the aspects of a company that can benefit from the implementation of business processes that are capable of being automated. High-volume jobs that are regular, time-sensitive, involve several individuals, and require compliance and audit trails are, in general, ideal candidates for automation. These tasks also need to be considered for automation.
The following are examples of use cases for business process automation solutions:
- New hires. A new hire's integration is a crucial business process that calls for a number of tedious but low-level duties. These consist of completing tax paperwork, organizing training sessions, filling out employee applications, and establishing direct deposit of paychecks. Process automation guarantees that all procedures are performed, reduces paperwork significantly, and updates relevant management and staff. There are several advantages to automating the onboarding process in terms of hiring and keeping staff.
- New Clients. As part of the Know Your Customer Rule 2090 obligations, financial services providers like as banks, insurers, and other lending firms must run background checks on potential new clients and notify the relevant local and federal government organizations upon onboarding. By automating numerous manual operations with artificial intelligence (AI), Business Process Automation can contribute to the streamlining of various procedures. Customer satisfaction is also increased by quicker, more automated operations.
- Help desk for information technology (IT). Most of the time, the number of incoming IT tickets exceeds the ability of IT personnel to manage them. Among other essential functions, automation software can evaluate, categorize, and forward incoming tickets to the appropriate support staff, notify customers of service upgrades, and notify IT staff of concerns that require rapid attention for compliance-related reasons. Artificial intelligence is used in advanced automated helpdesk technologies to anticipate, handle, and fix common user problems.
- Marketing Automation. Using marketing automation software, businesses can generate sales leads by sending automated marketing communications to customers through many channels, including email, websites, social media, and text messages. A subset of customer relationship management, or CRM, is the technology. Marketing departments often utilize it to boost overall marketing efficiency by eliminating repeated processes from staff workflows.
For more information about automating your business - Contact our specialists at PNATC. We walk you through the process. Contact us today for a free consultation.
Business Process Automation Positives
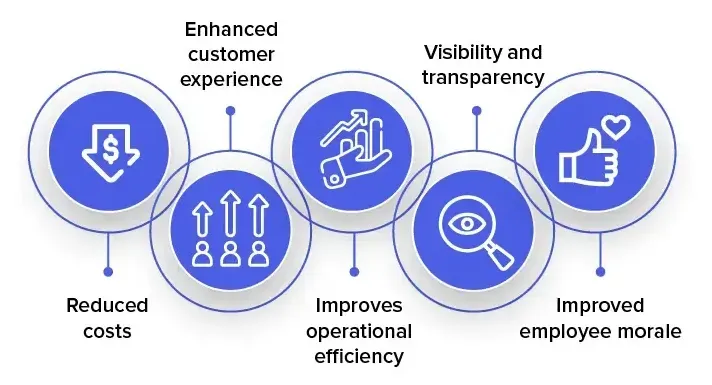
Business Process Automation (BPA) promotes uniformity and efficiencies, which in turn provide a host of commercial advantages.
- An increase in production.
- decreased expenses.
- lower incidence of human mistake.
- increased employee morale.
- Increased earnings.
- greater client support.
- understanding of process successes and shortcomings.
- enhanced compliance and monitoring.
- simple administration of compliance.
Automating repetitious processes that were previously performed by people results in time savings and a reduction in errors. In order for firms to accomplish this, they need to meticulously describe the stages that comprise their processes and allow for a limited amount of interpretation. In addition to this, the process automation system is required to communicate any exceptions that allow for human intervention. Employees are able to focus on higher-value work when workflow automation is used to automate menial chores.
Through the use of automation, businesses are able to gain insight into their workflows, which is another benefit of centralizing business processes. There is business process automation software that enables businesses to view all of the process phases on a single dashboard. This software ensures that businesses have insight into the current status of process activities, ranging from task reviews to the approval process. As an additional benefit, automation can guarantee that compliance standards are adhered to.
As firms strive to transform themselves into digital enterprises,
BPA has become an increasingly crucial factor. The automation of processes is essential to digital transformation. This automation typically starts with the transformation of information into formats that can be read by computers, which is subsequently included into the automation of the entire organization.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Business Process Automation (BPA)
- Initial Investment and Cost. Implementing Business Process Automation often requires a significant upfront investment. This includes the cost of purchasing or subscribing to automation software, integrating new systems with existing infrastructure, and possibly upgrading hardware. Smaller businesses might find the initial costs daunting, and even larger enterprises need to carefully consider the return on investment (ROI) and how it aligns with their long-term strategic goals.
- Employee Training and Adaptation. One of the key challenges in implementing BPA is ensuring that staff are adequately trained to use new systems and processes. Resistance to change is a common human tendency, and some employees may feel threatened by automation, fearing job loss or reduced importance. Overcoming these concerns involves transparent communication about the benefits of BPA, offering comprehensive training, and demonstrating how automation can make their work more engaging and less tedious.
- Integration with Existing Systems. BPA systems need to seamlessly integrate with existing organizational systems and processes. This integration can be complex, especially in organizations with legacy systems or those using a patchwork of different software solutions. Ensuring compatibility and smooth data flow between different systems is crucial for the success of BPA initiatives.
- Scalability and Flexibility. As businesses grow and evolve, their BPA solutions need to be scalable and flexible enough to accommodate changing needs. A system that works well for a small or medium-sized business may not be adequate as the business expands. Planning for scalability and the ability to adapt to future requirements is essential in the initial stages of BPA implementation.
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns. With automation, a significant amount of sensitive data is processed and stored electronically, raising concerns about data security and privacy. Companies must ensure that their BPA solutions comply with relevant data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). They also need to implement robust security measures to protect against data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement. Implementing BPA is not a one-time task; it requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Businesses need to regularly assess the performance of their automated processes, identify areas for improvement, and update their systems accordingly. This continuous cycle ensures that the BPA system remains effective and aligned with the organization's evolving needs.
- Understanding and Mapping. Processes Accurately. Before automation can be implemented, there needs to be a thorough understanding and accurate mapping of existing business processes. This step is crucial to identify which processes are suitable for automation and how they can be optimized. Inaccurate or incomplete process mapping can lead to inefficiencies and even failure of the BPA initiative.
- Managing Expectations.
It’s important for businesses to manage expectations around what BPA can achieve. While BPA can bring significant improvements, it is not a panacea for all business challenges. Setting realistic goals and timelines, and communicating these effectively to all stakeholders, helps in aligning expectations and achieving satisfactory outcomes.
Implementing Business Process Automation is a complex endeavor that requires careful planning, strategic investment, and ongoing management. While the challenges are significant, they can be navigated successfully with the right approach. By considering these key challenges and factors, businesses can effectively implement BPA to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and stay competitive in the modern business landscape.
For more information about automating your business - Contact our specialists at PNATC. We walk you through the process. Contact us today for a free consultation.
Business Process Automation and Robotic process automation
Business process automation (BPA) is the umbrella name for a set of automation tools that help optimize and streamline business processes. A branch of business process automation (BPA) called robotic process automation (RPA) aims to automate the way people utilize software at work. Businesses find it appealing because it offers a rapid method for automating data entry and copying data between apps.
By clicking and scrolling through a business process, employees and engineers alike can capture the rough draft for a basic automation using RPA software. The development team turns these draughts into the finished apps. These foundational programs are then made impervious to modifications in application layouts and processes by the different RPA platforms.
To construct more complex automations, intelligent process automation (IPA) and digital process automation (DPA) integrate fundamental RPA skills with AI tools. For instance, natural language processing can translate numbers from invoices to fields in commercial systems, while optical character recognition can read printed text. Estimating insurance damages is one of the tasks that machine vision algorithms could accomplish. Other kinds of judgments a bot might have to make can be automated with the help of AI and machine learning techniques.
Another kind of BPA automation tool is low-code development platforms. Instead than simulating human progress through the user interface, these tools leverage application programming interface (API) access. They are able to perform better than conventional RPA programs because of this. A few low-code solutions are beginning to combine the simplicity of RPA programming with the speed of cloud API execution, such Microsoft's Power Automate.
BPA & BPM Relationship
- Complementary Roles: BPM and BPA complement each other. While BPM focuses on the overall management of business processes, BPA provides the technology to automate these processes. BPA can be seen as a tool within the broader framework of BPM.
- BPA as a Component of BPM: Often, the automation of processes (BPA) is a result of a BPM initiative. A company may undertake BPM to improve its processes and, during this process, identify specific tasks that can be automated for greater efficiency.
- Sequential Relationship: Typically, a business would first engage in BPM to understand and optimize its processes. Following this, BPA can be implemented to automate these optimized processes.
- Enhanced Efficiency and Effectiveness: When BPA is implemented in conjunction with BPM, it leads to more efficient and effective processes. BPM’s analytical and methodological approach combined with BPA’s technology-driven execution can significantly enhance organizational performance.
While BPM and BPA are distinct, they are intricately linked in the quest for improved business performance. BPM provides the framework and understanding necessary to optimize business processes, while BPA applies technology to automate these processes for increased efficiency and reduced costs. Successful organizations often integrate both approaches to achieve optimal operational excellence.
How does business process analysis and BPA interact?
Despite utilizing the same term, business process automation and business process analysis are complementary technologies. A component of business process automation is business process analysis. Its focus is on business process analysis, as its name suggests. To map and comprehend current operations, it employs a variety of manual and automated techniques.
When using the manual method, process specialists usually conduct interviews with business users and subject matter experts in order to create a process map. Process mining, process capture, and process intelligence are just a few of the technologies that are used in the automated method to achieve the same goals.
Process mining maps out business processes and differences in their execution by analyzing enterprise system logs. Process capture, also known as task mining, creates a map of processes across several applications by using machine vision to monitor an employee's screen. The use of both technologies in conjunction with analytics and business intelligence capabilities to achieve increased automation and insight is known as process intelligence, a concept that has recently gained popularity.
These more automated methods for mapping and evaluating processes automatically have recently been dubbed "enterprise business process analysis".
Ways for Automating Business Procedures
Prior to starting a BPA project, it's vital to comprehend the current process' operation, the reasons it makes sense for automation, and the necessary modifications. Here are a few essential first actions to take:
- Examine the company's inclination towards business automation. Support from important stakeholders is necessary for business process automation since it alters how work is completed. The degree of executive commitment required for a BPA project depends on the automation's breadth. It is necessary to keep workers informed: Whether the BPA project is a transformative automation endeavor intended to support a new business model or something as simple as scanning a paper form into an electronic format and forwarding it to the right person, employees affected by the automation need to be trained on the new workflow and made aware of the business value that BPA technology offers. It's crucial to let them know how the new automation might improve their jobs.
- Recognize the processes that you use and who could benefit from automation. Without knowing where you're coming from, it can be difficult to get where you want to be. Understanding the current process is crucial before implementing an automation solution. For many firms, it might be challenging to comprehend the business rules that govern the current business operations.
- Project scope should be determined by automation maturity. Businesses usually get the most out of BPA projects when they automate case management and other intricate, mission-critical procedures. Experts recommend that businesses with no prior automation expertise start small and focus on repetitive, rule-based processes like purchase orders, where the procedures are clear-cut and well-understood. This work can be made more automated with the aid of several process intelligence tools, including process mining and process capture.
- Get feedback on process stages to automate, optimize, and remove from important stakeholders. The proverb "Don't pave the cow path" is also widely used in the context of process automation. The theory is that automating a process that already exists without first analyzing how or where it should be changed would only make its shortcomings worse. The validity of this caution is up for debate, particularly among businesses hoping to gain rapid benefits from automation. BPA experts often feel that a current process should only be automated after examining how it could be made more efficient and gathering feedback from important stakeholders. Software engineer James Highsmith III, one of the original creators of the Agile Manifesto and a prolific writer on software development, claims that IT, development teams, and business analysts all contribute to the success of automation projects.
Software available for business process automation
A wide range of well-known and quickly developing business automation technologies are included in BPA, such as the following:
- Tools for workflow designed for business users with no background in coding.
- RPA, which builds software robots that imitate user interface interactions between humans and digital systems.
- Intelligent automation trains automation models that get better over time by using machine learning and other AI methods.
- DPA is a phrase used to describe how BPA tactics relate to the broader project of digital transformation.
Furthermore, the field of business process management software is changing due to the incorporation of RPA, AI, and low-code/no-code features by prominent BPM suppliers like Appian and Pega. These kinds of cutting-edge technologies support BPA tactics in a number of ways.
Giving non-developers access to no-code automation platforms, for instance, enables users to swiftly customize apps and automate operations without requiring developers or programmers to do so.
A business saves money and time by doing this. Additionally, AI and machine learning systems are capable of data analysis and the search for novel ideas that improve on current procedures.
For more information about automating your business - Contact our specialists at PNATC. We walk you through the process. Contact us today for a free consultation.
Leave a Reply
Contact PNATC
Contact - Website lead
Recent Posts

Share Post
Contact PNATC
Get all your questions answered and problems solved with our QuickBooks experts today!